Introduction
Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC) tools are becoming increasingly essential for legal professionals who need to navigate complex regulatory environments, manage risks effectively, and ensure compliance across various jurisdictions. Choosing the right GRC tool requires a comprehensive understanding of the GRC process lifecycle and the specific functionalities that cater to legal practice needs. This guide will help lawyers evaluate GRC tools by focusing on the process lifecycle and the core functions that are critical in a legal context.
Understanding the GRC Process Lifecycle
A robust GRC tool manages the entire process lifecycle, from coverage to analysis. Understanding these stages is crucial for selecting a GRC tool that aligns with your legal practice.
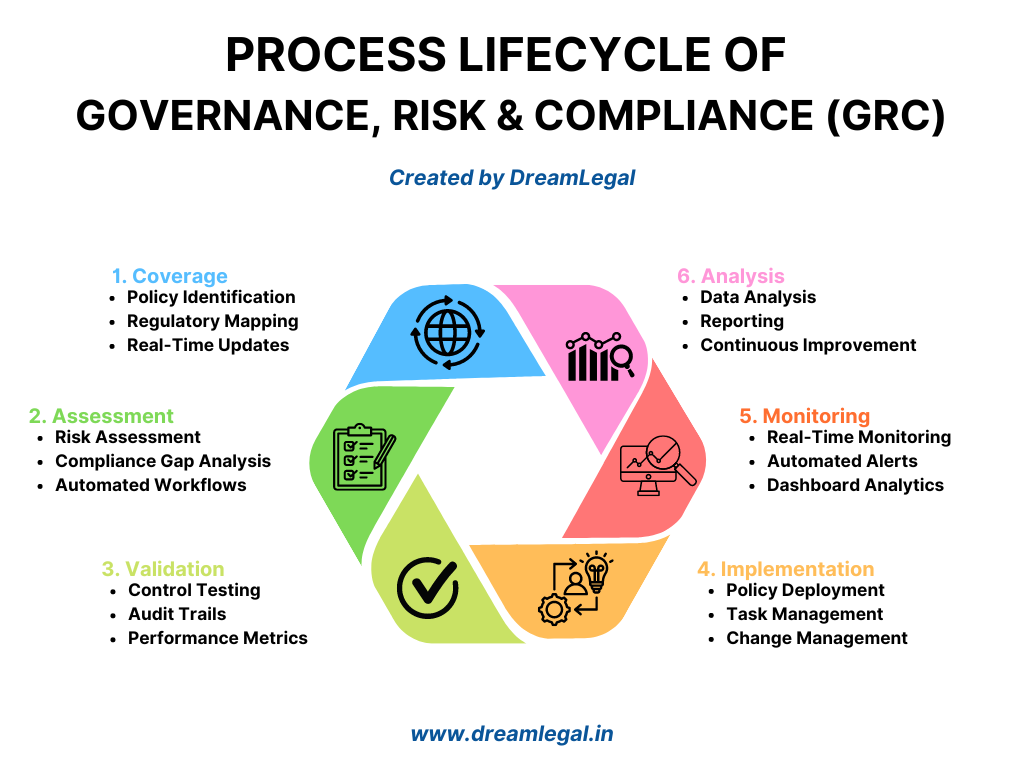
Coverage
The coverage stage involves identifying applicable laws, regulations, and internal policies. The GRC tool should simplify this process:
Key Features:
- Policy Identification: Automatically identifies relevant laws and regulations based on jurisdiction and sector.
- Regulatory Mapping: Links specific legal requirements to internal policies and controls.
- Real-Time Updates: Provides updates on new laws and regulatory changes.
For Law Firms: Large firms dealing with diverse clients across various sectors need comprehensive regulatory mapping and real-time updates to stay compliant and provide accurate legal advice.
For In-House Legal Teams: Corporate legal teams benefit from a GRC tool that integrates with existing compliance frameworks, ensuring that all applicable laws are tracked and adhered to across departments.
Assessment
In this phase, the GRC tool helps evaluate risks and compliance gaps within the organization.
Key Features:
- Risk Assessment: Identifies potential risks and evaluates their impact and likelihood.
- Compliance Gap Analysis: Detects areas where the organization fails to meet regulatory requirements.
- Automated Workflows: Streamlines the process of risk and compliance assessments with automated checklists and questionnaires.
For Startups: Startups need agile GRC tools that can quickly identify risks and compliance gaps, helping them establish strong governance frameworks without extensive resources.
For Government Departments: Government entities require thorough risk assessments to ensure public safety and compliance with stringent regulations.
Validation
Validation involves confirming the effectiveness of existing controls and processes. The GRC tool should facilitate this with robust monitoring capabilities.
Key Features:
- Control Testing: Verifies the effectiveness of controls in place.
- Audit Trails: Maintains a detailed record of all compliance activities and assessments.
- Performance Metrics: Tracks compliance performance over time, highlighting areas for improvement.
For Law Firms: Firms handling sensitive client data and financial transactions benefit from comprehensive audit trails and control testing features to maintain compliance and reduce risks.
For Enterprises: Large organizations need performance metrics to ensure compliance across multiple departments and jurisdictions, providing insights for continuous improvement.
Implementation
During the implementation stage, the GRC tool helps apply necessary changes to improve compliance and risk management.
Key Features:
- Policy Deployment: Distributes updated policies and procedures throughout the organization.
- Task Management: Assigns responsibilities for compliance activities and tracks progress.
- Change Management: Manages changes to policies, controls, and processes, ensuring smooth transitions.
For In-House Legal Teams: A GRC tool with strong task management and change management features ensures that compliance initiatives are implemented efficiently across departments.
For Startups: Startups benefit from automated policy deployment and task management, helping them maintain compliance without the need for extensive manual oversight.
Monitoring
Monitoring involves continuous observation of compliance status and risk levels. A GRC tool should provide real-time insights and alerts.
Key Features:
- Real-Time Monitoring: Provides continuous tracking of compliance status and risk exposure.
- Automated Alerts: Sends notifications for compliance breaches or emerging risks.
- Dashboard Analytics: Offers visual representations of compliance data for quick decision-making.
For Law Firms: Real-time monitoring and automated alerts help law firms manage multiple clients and cases, ensuring timely responses to potential compliance issues.
For Government Departments: Government agencies require robust monitoring tools to maintain transparency and accountability in their operations.
Analysis
The final stage involves reviewing and analyzing data to improve governance, risk management, and compliance efforts.
Key Features:
- Data Analysis: Analyzes compliance data to identify trends and areas for improvement.
- Reporting: Generates detailed reports on compliance activities, risk assessments, and policy effectiveness.
- Continuous Improvement: Provides recommendations for enhancing governance and compliance strategies.
For Enterprises: Large corporations benefit from comprehensive reporting and data analysis tools to drive strategic decision-making and improve compliance processes.
For Judiciary: Judicial bodies need data analysis tools to evaluate compliance with legal procedures and ensure fair administration of justice.

Evaluating Based on Practice Needs
Law Firms
- Focus: Comprehensive regulatory tracking, issue management, and real-time monitoring.
- Why: Law firms manage multiple clients across various jurisdictions, needing tools to track diverse regulations and ensure compliance.
- Key Features: Real-time monitoring, automated regulatory updates, incident reporting and tracking.
In-House Legal Teams
- Focus: Integration with existing enterprise systems, task management, and policy deployment.
- Why: In-house teams must align compliance efforts with organizational workflows across departments like HR, finance, and operations.
- Key Features: Enterprise integration, task assignment and tracking, organization-wide policy distribution.
Startups and Small Firms
- Focus: Cost-effective, scalable, and automated GRC tools.
- Why: Startups and small firms often have limited resources and need scalable solutions that grow with the business.
- Key Features: Automation of compliance tasks, scalable solutions, budget-friendly pricing.
Government Departments
- Focus: Data security, compliance tracking, and audit trails.
- Why: Government entities handle sensitive information and must comply with stringent regulations, requiring robust security and compliance tools.
- Key Features: Data encryption, compliance tracking, detailed audit trails.
Individual Practitioners
- Focus: User-friendly interfaces, compliance tracking, and policy management.
- Why: Solo practitioners need simple tools to manage compliance efficiently without overwhelming complexity.
- Key Features: Easy-to-use interface, compliance alerts, straightforward policy management.
Enterprises
- Focus: Customization, integration with enterprise systems, and comprehensive analytics.
- Why: Large corporations handle complex regulatory environments and need tools that support global operations and provide detailed insights.
- Key Features: Customizable workflows, system integration, advanced analytics.
Judiciary
- Focus: Secure document handling, compliance tracking, and transparency.
- Why: Judicial bodies need tools to ensure legal processes are fair, efficient, and adhere to legal standards.
- Key Features: Secure document storage, compliance monitoring, transparent audit trails.
Core Functions and Features of GRC Tools
When evaluating GRC tools, it’s important to assess how well they handle each stage of the process lifecycle while offering essential functionalities. Here are the core functions that legal professionals should focus on:
Policy Management
- Policy Creation: Tools for drafting and updating policies.
- Centralized Repository: Stores all policies in one location for easy access.
- Version Control: Tracks changes to policies over time.
- Policy Reviews: Regularly reviews and updates policies to ensure compliance.
- Policy Monitoring: Monitors adherence to policies and procedures.
Issue Management
- Incident Reporting: Facilitates reporting of compliance incidents and risks.
- Issue Assessment: Evaluates the severity and impact of reported issues.
- Action Tracking: Tracks actions taken to resolve issues and mitigate risks.
- Response Measuring: Measures the effectiveness of responses to compliance issues.
Laws, Compliance, and Regulatory Tracking
- Sectoral Relevance: Identifies laws and regulations relevant to specific sectors.
- Compliance Applicability: Assesses the applicability of laws and regulations to the organization.
- Law and Compliance Updates: Provides updates on new laws and regulatory changes.
Final Thoughts
Selecting a GRC tool requires careful consideration of how well it supports each stage of the process lifecycle and the specific needs of your legal practice. By focusing on core functions like policy management, issue management, and regulatory tracking, you can choose a GRC tool that optimizes governance, reduces risk, and enhances compliance, ultimately leading to more efficient and effective legal operations.
CHECK OUT GRC ON DIRECTORY: CLICK HERE


