Introduction
E-discovery tools have become indispensable for legal professionals managing electronic data for litigation, regulatory compliance, and investigations. Selecting the right e-discovery tool requires an understanding of the e-discovery process lifecycle and evaluating key functionalities tailored to legal practice needs. This guide will help lawyers assess e-discovery tools by focusing on the discovery process and the features that matter most in a legal setting.
Evaluating the E-Discovery Process Lifecycle
A robust e-discovery tool manages the entire discovery process, from data identification to presentation. Understanding these stages is crucial for selecting a tool that aligns with your legal practice.
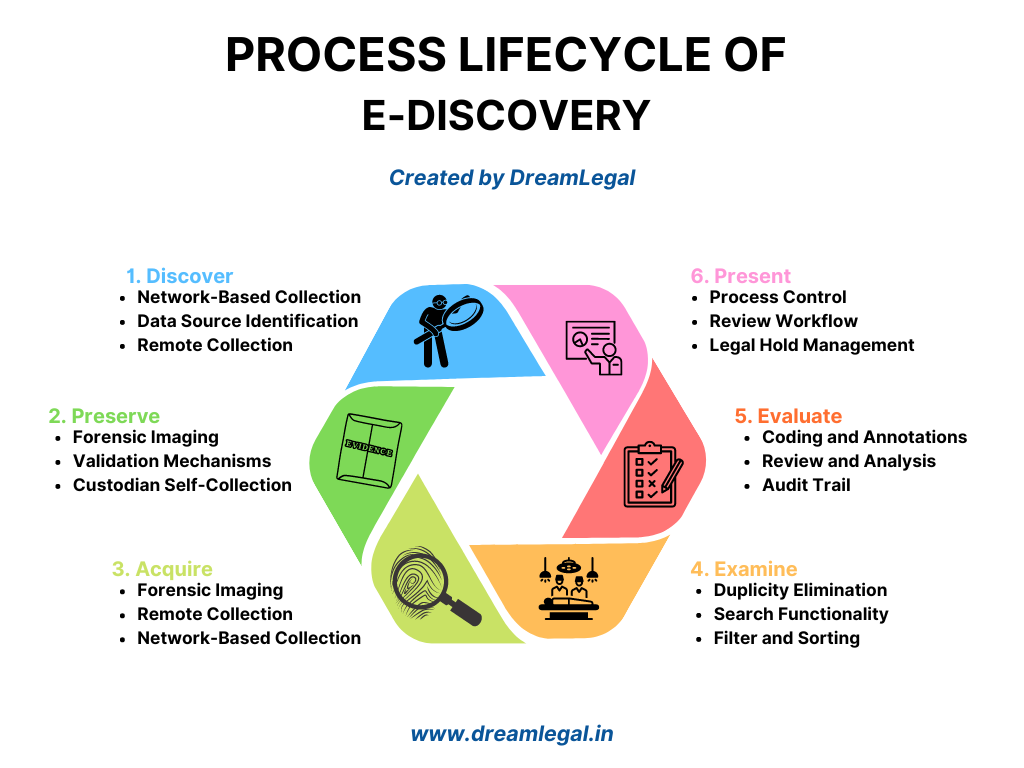
Discover
The discover stage involves identifying and locating relevant electronic data. The e-discovery tool should streamline this process:
Key Features:
- Data Source Identification: Identifies all potential sources of relevant data.
- Remote Collection: Allows for the collection of data from remote locations.
- Network-Based Collection: Gathers data across networks and systems.
For Law Firms: Firms handling complex litigation need robust data identification tools to quickly locate all relevant information across multiple data sources.
For Enterprises: Large organizations require network-based collection to manage data spread across different systems and departments.
Preserve
During this phase, the e-discovery tool ensures that data is preserved in its original state to prevent spoliation.
Key Features:
- Forensic Imaging: Creates exact copies of data for analysis without altering the original.
- Custodian Self-Collection: Allows data custodians to collect data themselves under controlled conditions.
- Validation Mechanisms: Ensures data integrity and authenticity throughout the preservation process.
For Government Departments: Government entities need forensic imaging and robust validation mechanisms to comply with strict data preservation regulations.
For In-House Legal Teams: Corporate legal teams benefit from custodian self-collection to efficiently manage internal investigations and compliance checks.
Acquire
The acquire stage involves collecting the identified data for further analysis. The e-discovery tool should support various collection methods.
Key Features:
- Remote Collection: Facilitates data collection from offsite locations.
- Network-Based Collection: Supports comprehensive data gathering from internal networks.
- Forensic Imaging: Ensures collected data is an exact replica of the original.
For Law Firms: Firms dealing with international clients benefit from remote collection features that facilitate cross-border data acquisition.
For Startups: Startups need flexible acquisition methods to handle data from various sources without the need for extensive in-house infrastructure.
Examine
Examination focuses on processing and filtering the collected data to identify relevant information. The e-discovery tool should provide robust analysis capabilities.
Key Features:
- Search Functionality: Allows for comprehensive search across data sets.
- Filter and Sorting: Helps narrow down relevant data quickly.
- Duplicity Elimination: Removes duplicate files to streamline the review process.
For Law Firms: Advanced search and filter capabilities help firms quickly pinpoint relevant information, reducing the time and cost associated with large-scale data review.
For Judiciary: Judicial bodies require duplicity elimination to ensure efficient data management and avoid redundant reviews.
Evaluate
The evaluation stage involves reviewing and analyzing the data to prepare for production. The e-discovery tool should facilitate an organized and efficient review process.
Key Features:
- Review and Analysis: Provides tools for thorough examination of data.
- Coding and Annotations: Allows users to mark up documents with relevant notes and categorizations.
- Audit Trail: Maintains a record of all actions taken during the review process.
For Enterprises: Large corporations benefit from comprehensive review and analysis features to manage complex litigation and compliance reviews.
For Individual Practitioners: Solo practitioners need coding and annotation tools to efficiently handle document review without additional staff.
Present
The final stage involves preparing and presenting the data for legal proceedings or compliance audits. An e-discovery tool should make this process seamless and accurate.
Key Features:
- Process Control: Ensures consistent handling of data throughout the e-discovery process.
- Review Workflow: Supports structured workflows to manage document review and production.
- Legal Hold Management: Manages legal holds to prevent data spoliation during litigation.
For Law Firms: Legal hold management and process control are critical for ensuring compliance with discovery obligations and avoiding sanctions.
For Judiciary: Judicial bodies require structured review workflows to maintain orderly and transparent case management.

Evaluating Based on Practice Needs
The requirements of an e-discovery tool vary depending on the type of legal practice. Below is a guide on how to evaluate e-discovery tools based on specific legal practice needs:
Law Firms
- Focus: Data identification, review, and production.
- Why: Law firms handle large volumes of data and need tools that streamline identification, review, and production to manage costs and meet deadlines.
- Key Features: Data source identification, review workflow, audit trail.
In-House Legal Teams
- Focus: Legal hold management, compliance, and review.
- Why: In-house legal teams require robust legal hold management and compliance features to protect against data spoliation and regulatory penalties.
- Key Features: Legal hold tracking, process control, custodian management.
Startups and Small Firms
- Focus: Cost-effectiveness, ease of use, and flexible data collection.
- Why: Startups and small firms often have limited resources and need affordable tools that are easy to use and support flexible data collection methods.
- Key Features: Remote collection, simple interface, custodian self-collection.
Government Departments
- Focus: Data preservation, compliance, and secure collection.
- Why: Government departments manage sensitive information and must ensure secure, compliant data collection and preservation practices.
- Key Features: Forensic imaging, validation mechanisms, legal hold management.
Individual Practitioners
- Focus: Efficiency, simplicity, and thorough review.
- Why: Solo practitioners need tools that streamline the e-discovery process and provide robust review capabilities without complex setup.
- Key Features: Coding and annotations, duplicity elimination, review workflow.
Enterprises
- Focus: Scalability, integration, and comprehensive analysis.
- Why: Large corporations handle extensive data and require scalable solutions that integrate with existing systems and offer advanced analysis features.
- Key Features: Network-based collection, cluster similar documents, advanced search functionality.
Judiciary
- Focus: Accuracy, transparency, and compliance.
- Why: Judicial bodies need tools that ensure accurate data handling, maintain transparency, and comply with legal standards during litigation.
- Key Features: Process control, audit trail, legal hold tracking.
Core Functions and Features of E-Discovery Tools
When evaluating e-discovery tools, it’s important to assess how well they handle each stage of the discovery process while offering essential functionalities. Here are the core functions that legal professionals should focus on:
Data Identification and Collection
- Data Source Identification: Locates all relevant data sources for discovery.
- Remote Collection: Collects data from remote locations efficiently.
- Network-Based Collection: Gathers data across internal networks.
- Forensic Imaging: Creates exact data copies for analysis.
- Custodian Self-Collection: Allows controlled data collection by custodians.
- Validation Mechanisms: Ensures data integrity and authenticity.
Search, Processing, and Analysis
- Search Functionality: Enables comprehensive search across data sets.
- Filter and Sorting: Helps narrow down relevant data.
- Duplicity Elimination: Removes duplicate files to streamline review.
- Data Processing: Prepares data for analysis by converting formats and extracting metadata.
- Cluster Similar Documents: Groups similar documents for easier review.
Review and Production
- Review and Analysis: Tools for examining data thoroughly.
- Coding and Annotations: Allows marking and categorizing of documents.
- Process Control: Manages consistent data handling.
- Review Workflow: Supports organized document review processes.
- Audit Trail: Tracks all actions for compliance and accountability.
Legal Hold Management
- Legal Hold Tracking: Monitors active legal holds to prevent data deletion.
- Legal Hold Notice Management: Manages the distribution and acknowledgment of legal hold notices.
- Receipt Acknowledgement: Confirms receipt and understanding of legal holds.
- Data Custodian Management: Manages data custodians involved in the legal hold process.
Final Thoughts
Selecting an e-discovery tool requires careful consideration of how well it supports each stage of the discovery process and the specific needs of your legal practice. By focusing on core functions like data identification, review, and legal hold management, you can choose an e-discovery tool that optimizes data handling, enhances compliance, and ensures efficiency in legal proceedings. Different legal practices have unique needs—whether you’re part of a law firm, corporate legal team, or a solo practitioner. By evaluating these needs carefully, you can select an e-discovery tool that best supports your practice’s requirements while offering room for growth and improvement.
CHECK OUT E-DISCOVERY TOOLS ON DIRECTORY: CLICK HERE


