Introduction
Client Relationship Management (CRM) tools are essential for legal professionals looking to streamline client interactions, manage leads, improve case handling, and ensure better client satisfaction. Choosing the right CRM tool requires understanding the CRM process lifecycle and assessing key functionalities. This guide will help lawyers evaluate CRM tools by focusing on the client relationship process and the features that matter most in a legal setting.
Evaluating the CRM Process Lifecycle
CRM tools are built to manage the entire client relationship lifecycle, from intake to review. Understanding these stages and what each requires will help you evaluate which CRM tool is right for your practice.
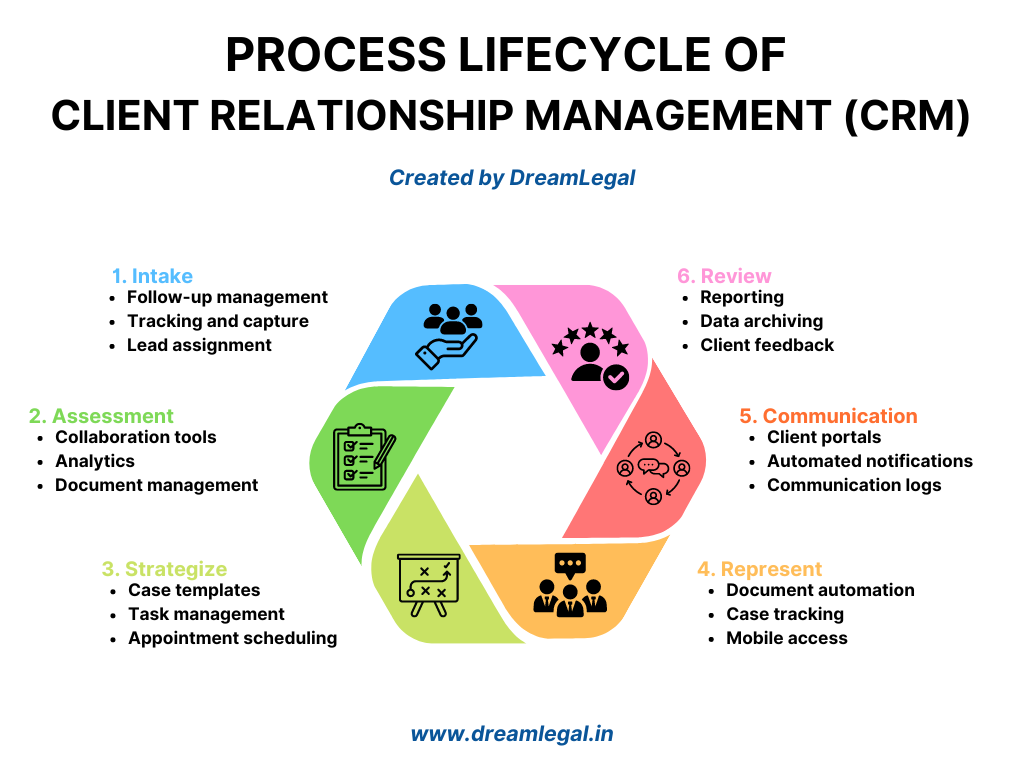
Intake
The intake stage involves capturing new client inquiries and leads. The CRM tool should simplify this process:
Key Features:
- Tracking and Capture: Automatically collects client details from web forms, emails, or phone calls.
- Lead Assignment: Routes inquiries to the appropriate lawyer or team member.
- Follow-up Management: Tracks and schedules follow-up actions to ensure potential clients are engaged.
For Law Firms: Firms handling multiple inquiries daily need a CRM that automates lead tracking and assignment, ensuring no lead falls through the cracks.
For Startups: Startups often need an agile CRM to capture leads efficiently without requiring extensive manual follow-up. Automation and lead assignment features are particularly valuable here.
Assessment
In this phase, lawyers evaluate the viability of new leads or potential cases. The CRM should help organize and streamline this process:
Key Features:
- Document Management: Allows storing and reviewing documents or evidence relevant to the client’s case.
- Collaboration Tools: Facilitates internal discussions on case potential.
- Analytics: Provides insights into case viability, client history, and risk factors.
For Law Firms: A robust document management system with categorization capabilities helps large firms review potential cases more efficiently.
For Individual Practitioners: Solos benefit from streamlined document storage and collaboration with external experts to quickly assess case viability without overwhelming the system.
Strategize
The strategy phase involves planning the case approach. The CRM tool should assist in setting up tasks, timelines, and collaboration spaces:
Key Features:
- Task Management: Assign tasks to team members and track their progress.
- Appointment Scheduling: Schedule meetings, court appearances, and deadlines.
- Case Templates: Provides pre-built templates for common legal strategies.
For In-House Teams: Corporate teams should prioritize a CRM that integrates task management with case-specific workflows, ensuring deadlines are met without cross-department miscommunication.
For Startups: Task management and case templates ensure that new teams stay on track, especially as they scale rapidly.
Represent
During the representation stage, lawyers actively manage the case, court appearances, and client communications. A CRM should centralize case details and streamline client interactions:
Key Features:
- Case Tracking: Provides real-time monitoring of all case-related activities.
- Document Automation: Streamlines the creation and submission of legal documents.
- Mobile Access: Ensures lawyers can access case files and update them on the go.
For Law Firms: Real-time case tracking and mobile access are critical for large firms where cases need to be managed by teams across multiple locations.
For Judiciary: Judiciary bodies require case tracking tools that maintain transparency and ensure timely document filing and communications.
Communication
Effective communication with clients is key to building trust and satisfaction. CRM tools should support ongoing, transparent communication throughout the case:
Key Features:
- Client Portals: Allows clients to securely access case updates and communicate directly with the legal team.
- Automated Notifications: Sends regular updates on case progress and important deadlines.
- Communication Logs: Maintains a record of all interactions for future reference.
For Law Firms: Client portals and automated notifications are essential for providing high-touch client service, especially when handling high-value clients.
For Individual Practitioners: Automated communications help solo lawyers keep clients informed without the burden of constant manual updates.
Review
After case completion, the CRM tool should facilitate a review of the case process, ensuring continual improvement in client relationship management:
Key Features:
- Reporting: Generates reports on case outcomes, time spent, and client feedback.
- Client Feedback: Gathers feedback from clients to assess satisfaction and areas for improvement.
- Data Archiving: Stores case data securely for future reference and compliance.
For Law Firms: Firms benefit from detailed reporting and feedback to improve service delivery and understand client trends.
For Enterprises: Large organizations benefit from client feedback and review processes to improve workflows and identify areas for better collaboration across departments.

Evaluating Based on Practice Needs
The requirements of a CRM tool vary depending on the type of legal practice. Below is a guide on how to evaluate CRM tools based on specific legal practice needs:
Law Firms
- Focus: Lead management, case alerts, and document management.
- Why: Firms handle multiple clients and cases simultaneously, requiring a CRM that automates lead capture, tracks case progress, and ensures no missed deadlines.
- Key features: Automated lead management, case alerts, document management.
In-House Legal Teams
- Focus: Integration with existing enterprise systems, collaboration tools, and expense tracking.
- Why: In-house teams work across departments, so seamless integration with CRM, ERP, and finance systems is crucial for maintaining efficiency and transparency.
- Key features: Enterprise integration, collaboration tools, expense tracking.
Startups and Small Firms
- Focus: Affordability, scalability, and automation.
- Why: Smaller teams need cost-effective solutions that grow as their client base expands, with automation to reduce manual administrative work.
- Key features: Cost-effective, scalable, automation.
Government Departments
- Focus: Data security, compliance, and case management.
- Why: Government entities need CRMs that prioritize security and regulatory compliance while managing sensitive client data effectively.
- Key features: Data security, compliance, case management.
Individual Practitioners
- Focus: User-friendly interfaces, lead management, and client communication.
- Why: Solo lawyers need simple tools that streamline client communication and case tracking without overwhelming them with complex features.
- Key features: User-friendly, lead management, client communication.
Enterprises
- Focus: System integration, comprehensive analytics, and scalability.
- Why: Large corporations handle numerous clients and legal matters, requiring a CRM that integrates well with other systems and offers robust reporting and analytics.
- Key features: System integration, analytics, scalability.
Judiciary
- Focus: Secure document handling, timeline tracking, and transparency.
- Why: Judicial bodies need CRM tools that ensure legal deadlines are met, case files are secure, and processes remain transparent and organized.
- Key features: Secure documents, timeline tracking, transparency.
Core Features and Functionalities to Consider
When evaluating CRM tools, it’s important to assess how well they handle each stage of the client lifecycle while also offering essential functionalities. Here are the core features that legal professionals should focus on:
Intake and Lead Management
- Tracking and Capture: Automatically captures leads from various sources.
- Lead Assignment: Distributes leads to the right team member based on skill or case type.
- Follow-up Management: Ensures timely follow-up actions to nurture potential clients.
For Law Firms: Firms that deal with large volumes of inquiries benefit from automated lead assignment and tracking features that ensure no potential client is missed.
Client Portal
- Profile Management: Allows clients to update their information and view case details.
- Appointment Scheduling: Provides clients the ability to schedule meetings and view upcoming appointments.
- Task Tracking: Clients can track tasks related to their case, such as document submission deadlines.
- Client Communication: Provides a secure channel for ongoing communication with the legal team.
For Individual Practitioners: A simple, intuitive client portal ensures effective communication without the need for frequent emails or calls.
Document Management
- Document Creation: Simplifies the creation of legal documents.
- Document Templatization: Offers ready-made templates for common documents.
- Version Control: Ensures that all document revisions are tracked and documented.
- Granular Permissions: Controls access to sensitive documents based on user roles.
For Enterprises: Strong document management with granular permissions is critical to ensure that only authorized personnel have access to sensitive client information.
Case Alerts
- Event-Based Notifications: Sends alerts when important case events occur (e.g., court dates, filing deadlines).
- Case Schedule Updates: Automatically updates schedules based on case developments.
- Document Change Alerts: Notifies relevant parties of any changes made to critical case documents.
For Law Firms: Automated notifications ensure lawyers never miss important deadlines, improving overall case management and client trust.
Budget, Expense, and Time Tracking
- Budget Management: Tracks case budgets and expenses to avoid overspending.
- Time Tracking: Logs time spent on tasks, ensuring accurate billing.
- Approval Management: Manages approvals for expenses and budgets.
For Startups: Startups benefit from automated time tracking and budget management to stay on top of financials, especially with limited resources.
Client Billing and Invoicing
- Multiple Fee Arrangements: Supports different fee structures such as hourly, flat fee, or contingency.
- Invoice Creation: Automates invoice generation based on time tracked and expenses.
- Automated Invoicing: Sends invoices automatically, reducing the chances of delayed payments.
For In-House Legal Teams: Automated invoicing ensures timely billing and reduces the workload on finance and legal departments.
Final Thought
When selecting a CRM tool, it’s essential to consider how well it supports each stage of the client relationship lifecycle, from intake to review. Different legal practices have unique needs—whether you’re part of a law firm, corporate legal team, or a solo practitioner. By focusing on lead management, client portals, document handling, and billing features, you can choose a CRM that optimizes client interactions, improves efficiency, and enhances overall service delivery.
Each practice area has its distinct priorities, and selecting the right CRM tool requires thoughtful evaluation to ensure it meets your firm’s specific requirements while offering room for growth and improvement.
CHECK OUT CRM TOOLS ON DIRECTORY: CLICK HERE


