Introduction
For startups, navigating legal complexities efficiently is essential for growth and success. Legal technology, or “legal tech,” provides digital solutions that help startups manage legal processes, stay compliant with regulations, protect intellectual property, and save costs. By leveraging legal tech, startups can focus on scaling their business while minimizing legal risks and administrative burdens.
Why Legal Tech for Startups?
- Efficient Contract and Document Management: Legal tech tools streamline the drafting, review, and management of contracts and legal documents, reducing errors and ensuring timely renewals.
- Regulatory Compliance: Automated compliance tools keep startups up-to-date with evolving laws, reducing the risk of penalties and ensuring legal adherence without a large legal team.
- Cost Savings: By automating routine legal tasks, startups can reduce reliance on expensive external legal counsel, saving money and resources.
- IP Protection: Legal tech platforms help manage intellectual property filings, monitor for potential infringements, and safeguard sensitive data.
- Faster Deal-Making: Tools like e-signatures and digital deal rooms facilitate quicker, more transparent transactions and agreements, essential for fast-paced startup environments.
- Enhanced Legal Research: AI-driven legal research tools provide quick access to relevant case law and regulations, supporting informed decision-making.
- Automating Administrative Tasks: Automation reduces the burden of repetitive legal tasks, allowing startups to focus on core business activities and growth.
How Startups Can Embrace Legal Technology
Startups face unique challenges in their early stages, from managing limited resources to navigating complex legal landscapes. Legal technology provides startups with the tools they need to operate more efficiently, reduce risks, and remain compliant, all while scaling their operations. Here’s a detailed guide for startups on how to adopt and integrate legal technology into their processes, allowing them to overcome their key challenges and set the foundation for sustainable growth.
Identifying Key Legal Challenges: Tailoring Solutions for Your Startup
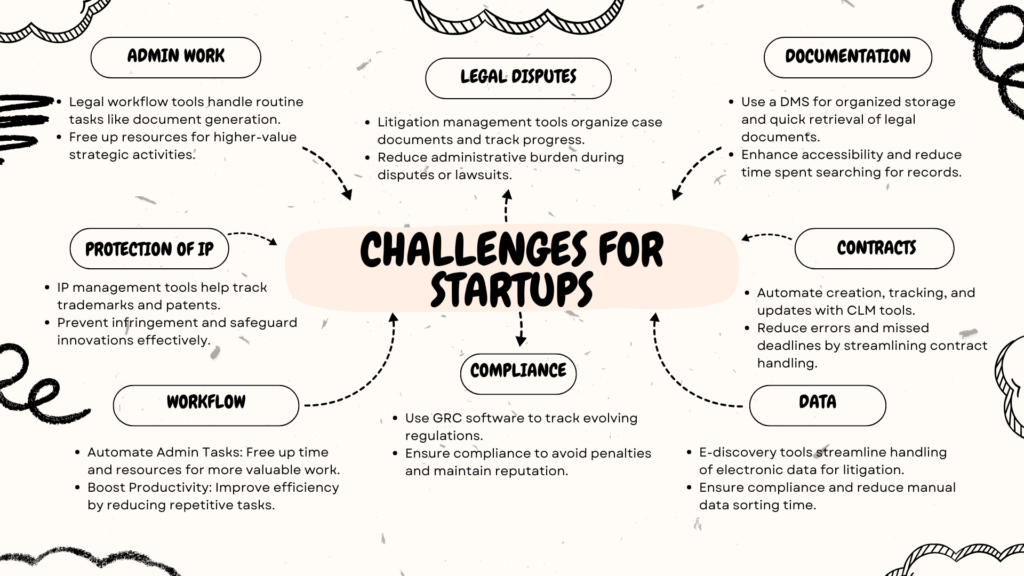
Startups often operate with limited resources, requiring a precise understanding of their key legal pain points to adopt the right technology solutions. Let’s take a closer look at the typical legal challenges startups face:
Kickstarting the Legal Technology Journey for Startups
For startups, adopting legal technology is crucial not only for ensuring compliance and managing risks but also for scaling operations efficiently as they grow. Legal technology helps startups navigate complex legal landscapes, streamline processes, and protect their intellectual property (IP). Here’s a step-by-step plan for startups to effectively integrate legal technology into their operations:
| Phase | Key Activities | Practical Insights for Startups |
| Phase 1: Foundational Assessment and Strategic Planning | 1. Identify Startup-Specific Legal Needs: Focus on core startup challenges such as contract management for investors and clients, protecting intellectual property (IP), ensuring regulatory compliance, and handling rapid growth in documentation.2. Map Out Lean Legal Workflows: Identify manual processes like drafting NDAs, employment agreements, IP filings, and regulatory checks that can be streamlined or automated to save time and reduce errors.3. Define Clear Goals: Set practical, startup-oriented goals, such as reducing contract review time by 60%, automating repetitive tasks (e.g., NDAs, agreements), and achieving 100% compliance with industry-specific data privacy regulations (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA). | – Prioritize Critical Legal Tasks: Startups should first focus on tools that immediately alleviate pain points, such as contract lifecycle management (CLM) for investor agreements or IP management tools for patent filings.- Adopt a Lean Tech Roadmap: Begin with essential tools like e-signature solutions (e.g., DocuSign, HelloSign) and basic document management systems (DMS), then scale up to more advanced compliance tools and AI-driven contract analytics as the startup grows. |
| Phase 2: Research and Solution Evaluation | 1. Identify Cost-Effective, Scalable Legal Tech Solutions: Look for tools that offer flexible pricing models (e.g., monthly subscriptions, per-user fees), ensuring they can grow with the startup. Consider SaaS-based solutions like Contractbook, Ironclad, or SeedLegals that require minimal setup and are cost-effective.2. Evaluate Must-Have Features: Prioritize tools that offer features like automated contract drafting, e-signature capabilities, GDPR/CCPA compliance modules, IP management, and easy integration with popular startup tools (e.g., Slack, Notion, HubSpot, cloud storage like Google Drive).3. Request Trials and Demos: Take advantage of free trials and demo periods to evaluate how well each tool fits into current workflows. Invite team members who will use the technology daily to provide feedback on usability and fit. | – Consider SaaS-Based Legal Tech Solutions: Startups should favor SaaS tools that offer low initial costs and scalability, allowing them to pay as they grow.- Involve Founders and Key Team Members in Evaluation: Decision-makers should include founders, early-stage team members, and legal advisors who understand the unique legal challenges faced by the startup.- Develop Startup-Centric Evaluation Criteria: Create criteria that focus on ease of use, scalability, pricing, customer support, and integration with existing startup tools like CRM, project management software, or collaboration platforms. |
| Phase 3: Pilot Testing and Initial Implementation | 1. Pilot Legal Tech Solutions in Critical Areas: Start with a high-impact area such as automating NDA processes for partnerships or managing investor agreements. This allows the startup to see quick wins and builds confidence in adopting legal tech.2. Monitor Key Metrics: Track KPIs like time saved per agreement, error reduction in legal documents, user adoption rates, and compliance adherence during the pilot phase. Use this data to adjust the solution to better meet startup needs.3. Customize Solutions Based on Startup-Specific Needs: Work closely with vendors to customize the tool for the startup’s unique processes, such as custom workflows for onboarding new clients or setting up tailored alerts for investor agreement deadlines. | – Choose a High-Impact Area for Pilots: Focus on areas where legal tech can show immediate results, such as automating the drafting and signing of standard agreements (NDAs, employment contracts) or streamlining IP management processes.- Appoint a “Tech Champion”: Designate a tech-savvy team member (e.g., a paralegal or operations manager) to act as a “tech champion” who can assist others in the transition, provide peer training, and collect feedback.- Encourage a Culture of Agility: Startups thrive on agility—pilot tests should allow for rapid iteration based on user feedback, focusing on refining the tech to fit startup dynamics. |
| Phase 4: Full Implementation and Training | 1. Gradual Rollout Across Teams: After a successful pilot, expand the implementation to other teams that handle legal documents or compliance tasks, such as sales (for client agreements), HR (for employee contracts), and finance (for compliance tracking).2. Ensure Seamless Data Migration: Transitioning from manual processes or basic legacy systems requires ensuring all critical legal data is migrated securely to the new platform. Collaborate with IT consultants or vendor support for data integrity.3. Conduct Tailored Training Sessions: Create focused, role-based training sessions to ensure each team knows how to use the technology effectively. For example, HR might focus on automated employment agreements, while finance focuses on compliance and investor reporting. | – Use a Phased Implementation Strategy: Start with the teams that are most impacted by legal processes, such as sales and HR, to ensure minimal disruption while maximizing benefits.- Provide Continuous Learning Opportunities: Offer ongoing support, including access to FAQs, webinars, and direct vendor support, to ensure the technology is utilized effectively.- Set Up a Support System: Assign a point of contact, like the “tech champion,” to coordinate with vendors for quick troubleshooting and user support. |
| Phase 5: Monitoring, Optimization, and Scaling | 1. Monitor Legal Tech Performance: Track key performance indicators such as user adoption rates, document processing times, contract error reduction, and overall user satisfaction. Conduct regular surveys to gather feedback on usability and potential improvements.2. Optimize Workflows Based on Feedback: If users find certain features cumbersome, work with the vendor to streamline or adjust them. For example, simplifying the process for uploading new contracts or adjusting notification settings for compliance deadlines.3. Scale Legal Tech Solutions: As the startup grows, scale up to more advanced tools such as AI-driven legal research (e.g., ROSS Intelligence), advanced compliance monitoring, or integrated IP management systems. Ensure legal tech integrates seamlessly with other business tools like CRM, ERP, or cloud-based project management software. | – Encourage Continuous Feedback and Improvement: Foster a culture where team members regularly provide feedback on tools and suggest improvements or new solutions.- Stay Agile and Adaptable: Regularly review the startup’s legal tech strategy to adapt to evolving business needs, industry regulations, or growth stages.- Stay Updated on Trends and Innovate: Keep an eye on the latest legal tech trends through startup accelerators, industry webinars, or tech forums to stay ahead of the competition and drive innovation. |
Phase 1: Foundational Assessment and Strategic Planning
- Identify Key Legal Needs and Challenges
- Conduct a Legal Needs Assessment: Start by identifying the most pressing legal needs that could be solved with technology. Common startup challenges include contract management, IP protection, staying compliant with industry regulations, and handling rapid document growth.
- Map Out Current Legal Workflows: Document the current workflows for handling legal tasks such as contract drafting, IP filing, compliance checks, and document storage. Identify manual, time-consuming processes that could be automated or optimized.
- Define Short-Term and Long-Term Legal Goals: Set clear, actionable goals for what the startup aims to achieve with legal tech. For instance, reducing contract review time by 60%, automating NDAs and employment agreements, or ensuring 100% compliance with data privacy regulations.
- Create a Lean Legal Tech Roadmap
- Develop a Strategic Plan for Legal Tech Adoption: Create a phased plan that focuses on quick wins and gradual scaling. Start with core tools like e-signature solutions and basic document management systems (DMS), and expand to more advanced tools like contract lifecycle management (CLM) and compliance tracking as the startup grows.
- Set a Realistic Budget and Timeline: Given limited resources, startups should allocate a budget that covers initial software costs, training, and minimal support. Create a timeline that includes immediate priorities (e.g., basic DMS) and future phases for scaling (e.g., advanced compliance tools).
Phase 2: Research and Solution Evaluation
- Research Legal Tech Solutions Tailored for Startups
- Look for Cost-Effective, Scalable Solutions: Focus on legal tech solutions that offer startup-friendly pricing, flexibility, and scalability. Consider SaaS-based solutions that provide a low entry cost and can scale as the company grows.
- Evaluate Core Features for Startups: Ensure that the solutions offer essential features like automated contract drafting, e-signature capabilities, data privacy compliance, IP management, and easy integration with other startup tools (e.g., CRM, cloud storage).
- Request Trials and Demos: Take advantage of free trials and product demos to understand how each tool fits into your existing workflows. Involve team members who will be primary users to provide feedback on usability and functionality.
- Engage Key Stakeholders in Decision-Making
- Involve Founders and Key Team Members: Given the lean nature of startups, involve founders, legal advisors (if any), and key team members in evaluating and selecting the right legal tech tools.
- Establish Evaluation Criteria: Develop a set of criteria that includes ease of use, scalability, integration capabilities, pricing, and customer support. Use these criteria to objectively assess each solution.
Phase 3: Pilot Testing and Initial Implementation
- Pilot Legal Tech Solutions in High-Impact Areas
- Choose a Pilot Focus Area: Select a critical area to pilot the legal tech solution, such as automating the Non-Disclosure Agreement (NDA) process or managing investor agreements. This allows the startup to see quick benefits and build confidence in the technology.
- Monitor Key Metrics During the Pilot: Track key performance indicators (KPIs) like time saved, error reduction, and user adoption rates during the pilot phase. Use feedback to make necessary adjustments.
- Customize Solutions to Fit Startup Needs: Work with the vendor to fine-tune the solution, ensuring it is adapted to the specific needs of the startup. Customization may include workflow adjustments, template creation, or integration with existing tools.
- Develop a Change Management Strategy for Early Adoption
- Communicate the Benefits Clearly: In a startup environment, everyone needs to be on board with new technology. Clearly communicate the benefits of the legal tech tool, such as time savings, reduced legal risks, and enhanced collaboration.
- Assign a “Tech Champion”: Appoint a tech-savvy team member to serve as a “tech champion” who will lead the adoption process, assist others, and collect feedback.
Phase 4: Full Implementation and Training
- Roll Out Legal Tech Solutions Across Teams
- Expand Gradually Across Departments: After a successful pilot, gradually roll out the solution to other teams that handle legal documents, contracts, and compliance tasks, such as HR, sales, and operations.
- Ensure Seamless Data Migration: If transitioning from manual or legacy systems, ensure that all critical data is migrated securely and accurately to the new platform. This may require collaborating with IT consultants or vendor support.
- Provide Focused Training for All Team Members
- Create Short, Focused Training Sessions: Conduct role-based training sessions tailored to how each team will use the technology. For example, HR might focus on contract automation for new hires, while the operations team might focus on compliance tracking.
- Offer Ongoing Learning and Support: Ensure continuous support through a combination of FAQs, user guides, and periodic training refreshers. Leverage vendor-provided resources such as webinars and online support.
- Set Up a Support System for Quick Troubleshooting
- Establish a Point of Contact for Support: Given the lean nature of startups, have a designated point of contact (like the tech champion) to coordinate with the vendor’s support team and address user issues promptly.
Phase 5: Monitoring, Optimization, and Scaling
- Monitor Performance and User Adoption
- Track Key Performance Metrics and User Feedback: Continuously monitor metrics such as user adoption rates, time savings, compliance adherence, and overall satisfaction. Regularly survey users to gather feedback on what is working well and what needs improvement.
- Use Feedback to Optimize Workflows: Make necessary adjustments to workflows based on feedback. For example, if users find certain features cumbersome, work with the vendor to simplify or adjust them.
- Scale Legal Tech Solutions as the Startup Grows
- Expand to More Advanced Features as Needed: As the startup grows, scale up to more advanced legal tech tools, such as AI-driven legal research, advanced compliance monitoring, or integrated IP management systems.
- Integrate with Other Business Tools: Ensure legal tech solutions integrate seamlessly with other business tools like CRM, ERP, or cloud storage to maximize efficiency and data consistency.
- Stay Updated on Legal Tech Trends and Innovate Continuously
- Encourage Continuous Learning and Improvement: Stay current with the latest legal tech trends by attending industry webinars, participating in startup accelerator programs focused on legal tech, and joining relevant communities.
- Foster a Culture of Innovation: Encourage team members to suggest improvements and explore new technologies that can help the startup stay agile and competitive.
- Conduct Regular Reviews and Adjust Strategies
- Schedule Regular Tech Reviews: Conduct periodic reviews to evaluate the performance of legal tech tools and adjust the technology strategy based on evolving business needs and goals.
Top 4 Most Useful Legal Tech for Startups
Startups, with their rapid pace of growth and need for efficiency, can greatly benefit from legal technology that helps streamline operations and reduce risks. Here are the four most useful legal technology categories that startups should consider adopting to address their key challenges.
Contract Lifecycle Management (CLM)
Contracts are a fundamental part of any startup, whether for partnerships, vendor agreements, or employee contracts. However, manually managing multiple contracts can quickly become overwhelming, leading to missed deadlines or overlooked clauses.
- Why It’s Useful: CLM platforms automate the process of creating, tracking, updating, and renewing contracts. They provide templates, track important dates like renewal or termination, and ensure compliance with contract terms.
- How Startups Benefit: Startups can reduce the time spent on contract management, mitigate risks associated with manual errors, and ensure all contracts are easily accessible and up-to-date.
Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC) Software
Startups operating in regulated industries, such as healthcare, fintech, or cybersecurity, face stringent compliance requirements. Navigating these regulations manually can lead to errors and non-compliance, putting the business at risk.
- Why It’s Useful: GRC software helps startups monitor regulatory changes, track compliance requirements, and manage risk more effectively. It provides real-time alerts, ensuring the startup stays compliant with relevant laws and standards.
- How Startups Benefit: By using GRC software, startups can avoid legal penalties, improve regulatory oversight, and operate confidently in highly regulated sectors without dedicating excessive resources to compliance monitoring.
Document Management System (DMS)
Startups generate a large volume of legal documents, from contracts and agreements to intellectual property filings. Organizing and accessing these documents efficiently is essential, especially as the startup grows.
- Why It’s Useful: A DMS centralizes all legal documents, allowing users to store, retrieve, and manage documents in one place. It includes version control, search functionality, and secure access, making document management more streamlined.
- How Startups Benefit: Startups save time and reduce the risk of lost or misfiled documents. A DMS also ensures that important legal records are easily accessible for audits, compliance checks, or legal disputes.
E-Signature Platforms
Obtaining signatures for contracts, approvals, or important documents is a frequent challenge for startups, especially when dealing with remote teams, clients, or investors. Delays in obtaining signatures can slow down operations and affect critical business decisions.
- Why It’s Useful: E-signature platforms allow startups to send, track, and obtain signatures electronically, eliminating the need for physical paperwork or manual processes. These platforms also provide secure, legally binding digital signatures.
- How Startups Benefit: E-signature tools streamline the signing process, reduce delays, and ensure faster execution of agreements. This helps startups move quickly and keeps business operations on track, even when approvals are needed from multiple stakeholders
Conclusion
Legal technology is an essential component of a startup’s toolkit, providing the efficiency, protection, and compliance necessary for sustainable growth. By conducting a thorough needs assessment, selecting the right tools, implementing technology effectively, and ensuring team buy-in, startups can embrace legal technology to streamline their operations and mitigate risks. As the startup grows, remaining agile and continuously optimizing legal tech solutions will be key to future success.


